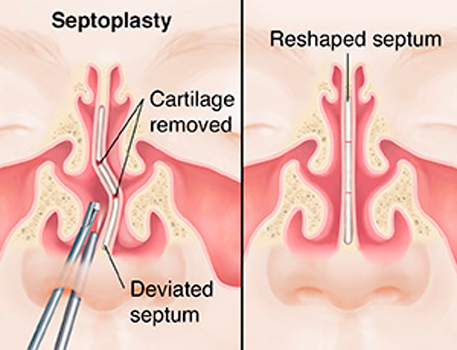
- The nasal septum is the piece of cartilage that divides the inside of the front of the nose into two compartments. Often, it is bent to one side and can block the nose.
- Septoplasty and submucosal resection of the septum are performed to straighten the nasal septum. These procedures may also be a part of other operations, such as endoscopic sinus surgery or septorhinoplasty.
- The operation is usually performed as a day-case procedure under local or general anaesthetic. Occasionally, it is necessary to stay in hospital overnight if there is a lot of bleeding and your nose has to be packed.
- A local anaesthetic solution is injected under the skin lining the nose, via the nostril. This raises the lining and reduces bleeding. The lining is lifted up on one or both sides, and the bent parts of the septum are removed (submucosal resection)or reshaped (septoplasty)to give a flat surface. The lining is then replaced and an absorbable stitch used to close the wound.
- Usually, pain is mild and easily controlled with simple painkillers. It is advisable to take a week off work after the operation, and you should not do any heavy lifting for about a week.
- The difference between septoplasty and submucosal resection is that septoplasty preserves as much cartilage as possible. It is generally preferred to submucosal resection nowadays.
